Chapter 1. Define Cloud Computing
Cloud computing – Delivering computing services over the internet.
Traditional IT – Virtual Machines, Storage, Databases, Networking are owned by the organization and accessed form an On-Premise location.
Cloud Enabled IT – Virtual Machines, Databases, Networking, Internet of Things (IoT), Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) services are offered by a Cloud Service Provider (CSP). Customers rent these services from the CSP.
Chapter 1 Study Resources:
Chapter 2. Describe the shared responsibility model
Shared Responsibility Model – Responsibilities are shared between the cloud provider and the costumer.
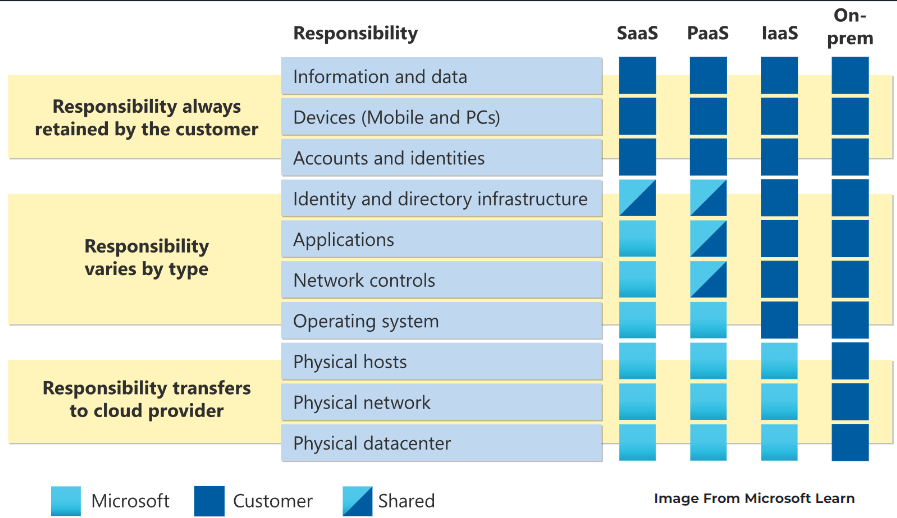
Chapter 2 Study Resources:
Chapter 3. Define cloud models, including public, private, and hybrid
Cloud models – Deployment types for cloud resources.
| Cloud Model Type | Definition |
| Private Cloud | Privately owned cloud, owned by a single entity. |
| Public Cloud | Ownded by a 3rd party cloud provider. Anyone can purchase and use resources |
| Hybrid Cloud | Both public and private cloud. Inter-conencted environment |
| Multi-Cloud | Mutliple public cloud providers |
| Azure Arc | Manage your cloud environemnts |
| Azure VMware | Integrate with your existing VMware workloads |
Chapter 3 Study Resources:
Chapter 4. Identify appropriate use cases for each cloud model
| Cloud Model Type | Use Case |
| Private Cloud | Used by a Single Entity Much Greater Control Greater Cost |
| Public Cloud | Used by Everyone Built, controlled, and maintained by CSP Cost is relative to usage |
| Hybrid Cloud | Both Public and Private Clouds are used Constant private usage and temporary public usage |
| Multi-Cloud | 90% of large organizations use multi-cloud Use multiple public cloud providers(Azure,AWS,GCP) Ability to use different cloud features |
| Azure Arc | Central Control Manage your Cloud Environments Private Cloud, Hybrid Cloud or Multi-Cloud |
| Azure VMware | VMWare Private Cloud VMware Workloads in Azure |
Chapter 4 Study Resources:
Chapter 5. Describe the consumption-based model
Consumption-based Model – Pay for the IT Resources you use. Stems from the OpEx Model.
OpEx – Operational Expenditure
CapEx – Capital Expenditure
Consumption-Based Model Benefits:
- No upfront costs.
- No purchase of infrastructure
- Access more resources as needed
- Stop resources that are no longer needed
- Pay during a billing period
| Consumption-Based Model | Subscription-Based Model |
| Pay for actual usage | Pay a fixed fee for a set package of services |
| Highly scalable, adjust usage as needed | Limited to the resources in the package |
| Less predictable, varies with usage | More predictable, fixed cost |
| Variable workloads, temporary spikes | Steady workloads with predictable usage |
Chapter 5 Study Resources:
Chapter 6. Compare cloud pricing models
Cloud pricing models – Various options to pay for cloud services
| Cloud pricing model | Explanation |
| Pay-as-you-go | Charged for what you use Prices determined per hour or per minute No upfront commitment Users can scale services up or down as needed Monitor cost in real time |
| Reserved Instances | Reserve resource for a specific term Committed resource usage Receive a discounted rate for committed resources |
| Spot Pricing | Accessing unused Azure compute capacity Significant Cost Savings Temporary Use cases Not meant for production Can be reclaimed at anytime |
| Dev/Test Pricing | Dev/Test workloads Reduced pricing Visual Studio Subscription |
| Free Tier | Free services for up to 12 months Limited amount of services No commitments |
| Hybrid Benefits | Existing Microsoft Licences used in Azure environment Windows Server, SQL Server licenses or Linux subscriptions |
Chapter 6 Study Resources:
Chapter 7. Describe serverless
Serverless – Build, deploy, and operate applications without infrastructure. Infrastructure is present, just abstracted from the user.
Serverless Computing Main points:
- Serverless compute is offered through a model called Functions as a Service
- Functions are snippet of Codes
- Customers are charged for the time their code runs
- Teams can focus on business logic and bringing value faster
- Cloud service provider provisions, scales, and manages the infrastructure
- Azure functions, Logic Apps and Event Grid falls under Serverless
- Azure functions is the main FaaS offering
- Azure has serverless solutions for Compute, DevOps, Database and Storage serivces
Chapter 7 Study Resources: